Everything you need to know about Artificial Insemination in Dogs
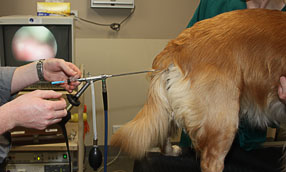
Artificial insemination is the process of artificially inserting sperm into a female vaginal or cervix in order to induce pregnancy. This method has been used in cattle for decades, but it has only recently gained popularity among dog breeders. Expert inseminators or practising veterinarians are usually the ones to do it.
For
centuries, artificial insemination has been used mostly in cattle. Initially,
dog breeders were hesitant to use the method, but the trend has already caught
on in the canine world. The rising need for artificial insemination, as well as
breakthroughs in semen technology, encouraged this trend. Simply defined, this
is the method of breeding dogs without mating them by injecting sperm into the
dam's vaginal canal when she is ovulating to aid conception.
The semen can be used directly, chilled in the fridge, or frozen. When the female dog is ovulating, a syringe containing the semen is injected into her cervix. Insemination can also be performed surgically or with a trans-cervical endoscope.
Artificial
Insemination Procedure in Dogs
Artificial
Insemination is about choosing the best male to collect the sperm from. The
male dog should have the desired intelligence, personality, and other
characteristics. A female teaser is brought near him once he has been chosen.
If there is no female dog on heat, a cotton swab that is scented like a female
in estrus can be used to entice the male. His penis is diverted to an artificial
vagina where the semen is harvested when he tries to mount the female.

The
semen is then discharged through a plastic or glass straw that is inserted into
the female vagina. A plastic or glass pacifier containing sperm is then
inserted into her vagina and the sperm is released. More complex insemination
methods involve inserting a tiny endoscope into the vagina and using it to
guide a straw through the cervix and into the uterus.
A
veterinarian or you can do it at home. By bringing both the male and female dog
into the same room, allow the male to try to mount the female while keeping the
artificial vagina nearby. The artificial vagina must be put over the male penis
when he begins to mount in order to catch the seminal fluids.
Artificial
insemination in dogs is very frequent among dog breeders who try to add other
traits to their breed. The male is selected for his temperament, intelligence,
and ability to produce useful puppies, and is matched with females who are
capable of reproducing in normal circumstances. It entails obtaining a male
dog's or stud's sperm and transferring it to a female dog's reproductive
system.
In
the female dog's vagina, insert the 1.4-inch tube. The breed size of your dog
will determine how many tubes should be inserted. For pups that weigh less than
5 pounds, it's best to have your vet perform the procedure. For small breeds
like Chihuahuas and Pomeranians, insert the tube just 2-inch. For bigger breeds
like German Shepherds and Great Danes, only a 5-inch tube insert is
recommended.
Insert
the syringe in the opposite end of the tube that has been inserted into the
vaginal canal of the female dog. Gently push the plunger down until all of the
seminal fluids have been deposited into the tube, then hold the tube erect to
ensure that the fluids are delivered and do not leak.
Dog Artificial
Insemination Success Rate
Lazzaro
Spallanzani, an Italian Catholic priest, physiologist, and biologist, performed
the first animal artificial insemination in 1780. He was studying animal
reproduction when he came up with the idea of canine artificial insemination.
According
to an article on BBC news, the success rate of artificial Insemination is over
50 percent. This is an average success rate; however, the actual number depends
on the quality of the semen. Fresh semen is basically the best. If an
experienced and skilled breeder performs the procedure, the success rate is
around 80 percent. This percentage drops to 59 -80 percent if the semen is cold
and then 52-60 percent if the semen is frozen. Storing semen can damage its
viability and eventually the breeding outcome. Frozen semen is processed before
it is mixed with a preservative and then frozen with liquid nitrogen. This
process can greatly affect semen quality.
When
it comes to artificial insemination, timing is important. The fertile period is
very short. You have just a few days to breed the dog. For fresh semen,
artificial insemination is best done 2 days after ovulation and 3-4 days after
ovulation for frozen semen. There are many methods for determining whether or
not your dog is ovulating. Progesterone testing is the most common, and it is
done every two days to ensure accurate results.
Regarding
how often a dog should be inseminated, there are different schools of thought.
According to the study published in PubMed, you will get better results with
two inseminations than with one insemination. The research included 36 female
dogs that were inseminated with frozen semen. Some were inseminated once and
others twice a day or twice. The average pregnancy rate was 67 percent with a
litter size of 6.4. Those inseminated once had a pregnancy rate of 64 percent,
while those vaccinated twice had a pregnancy rate of 69 percent.
Benefits of
Artificial Insemination
Artificial
Insemination is beneficial since it makes it easier for breeders to diversify
their genetic pool. In the past, a female dog had to be transported across the
border to mate with the desired male. Now, the semen of a male dog can be
collected from anywhere in the world, stored, and transported. Genetic pool
expansion is particularly helpful for dog breeds that are found in small
numbers in certain geographic locations.
Breeders
can also use artificial insemination to improve kennel genetics. They can
choose from a variety of sources, including semen from deceased dogs. The
process also allows for the examination of semen for fertility and
abnormalities. It also protects against sexually transmitted infections.
The
process decreased stress levels for both animals as there is no need for travel
or trauma attributable to mating
Weaknesses
of Artificial insemination in dogs
The
weaknesses of using canine artificial insemination depend heavily on the type
used, the unique considerations, and the procedure method. The following are
the weaknesses of canine artificial insemination.
- Possible
risk of wasting expensive semen if corners are cut by the vet or breeders.
- Failure due to poor clinical examinations of the breeding pair
- Frozen semen must be stored and thawed properly to maintain its viability
- There's a chance that artificial insemination will be used for the wrong motives.










No comments: